1. Causes of Gout
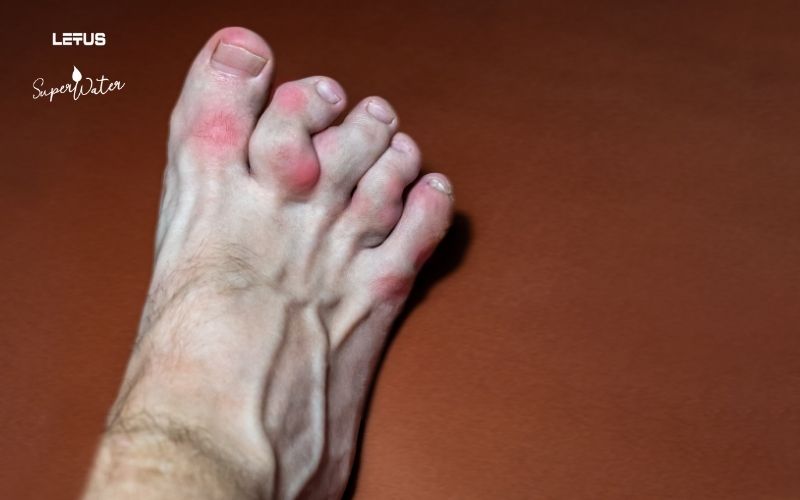
Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood, passes through the kidneys, and is excreted in the urine. However, Gout occurs when the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys excrete too little. In such cases, uric acid accumulates and deposits as Urate crystals in the joints or surrounding tissues, leading to the disease.
Uric acid is the final product of Purine metabolism in humans, and its concentration is mainly determined by endogenous metabolism (synthesis and cell turnover), as well as the rate of renal excretion and reabsorption [2]. Humans lack uricase, the enzyme responsible for converting uric acid into a more soluble and excretable form. Renal urate underexcretion accounts for the majority of hyperuricemia (high uric acid) and Gout [3].
The causes of Gout are divided into two types: primary (the majority of cases) and secondary (only a few acquired cases).
Primary Gout Causes:
- 95% of cases occur in men, typically aged 30-60.
- A diet rich in purine-containing foods such as protein and seafood: liver, kidney, shrimp, crab, egg yolks, mushrooms, etc., is considered to worsen the disease.
- Frequent, heavy alcohol or beer consumption.
- Regular consumption of high-fructose beverages, such as soda, carbonated soft drinks, and a diet excessively high in sugar.
Secondary Gout Causes:
- A family history of Gout.
- Due to increased production of uric acid, decreased excretion of uric acid, or both.
- Kidney failure and other conditions that impair the renal glomeruli’s uric acid excretion process.
- Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, impaired kidney function, heart disease, atherosclerosis, vascular occlusion, infectious diseases, and hypertension.
- Blood diseases such as acute leukemia.
- Use of certain medications that cause the body to accumulate uric acid, such as: Aspirin, Diuretics, Chemotherapy drugs, and immunosuppressants like cyclosporine, etc.
- Use of cytotoxic drugs to treat malignant diseases.
- Use of anti-tuberculosis drugs such as: ethambutol, pyrazinamide, etc.
- Recent injury, surgery, or dehydration.
2. What are the Symptoms of Gout?
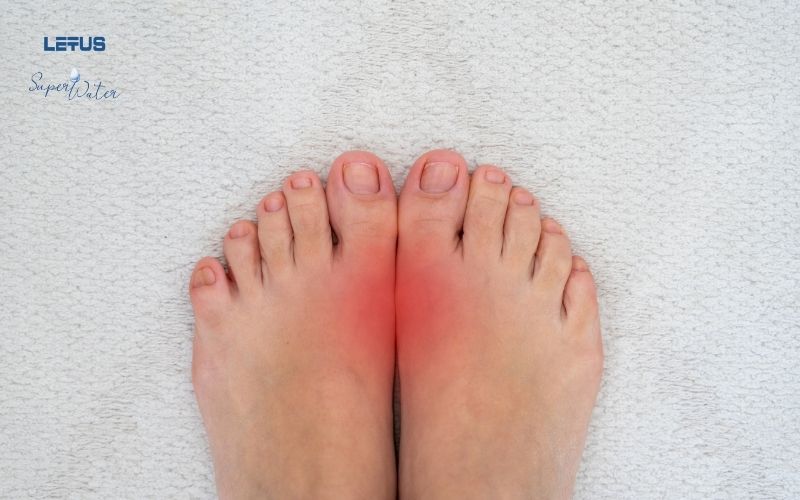
Manifestation
Gout typically presents with basic symptoms of sudden pain (often at night) in the joint connecting the big toe to the foot. However, the top of the foot, ankle, knee, wrist, and elbow are also common sites of pain.
The pain often lasts for several hours and is very intense, accompanied by swelling, heat, redness, and sensitivity to touch, sometimes leading to infection.
The skin over the affected joint will be tense, hot, shiny, red, or slightly purplish. Many cases may also involve fever, rapid heart rate, chills, and fatigue.
Stages of Symptoms
Early Stage:
This stage has few noticeable symptoms. A blood test will show elevated uric acid levels, often accompanied by pain and swelling/redness in the toe, ankle, knee, wrist, and finger joints. Symptoms become more pronounced after sports, strenuous activity, or following events involving heavy consumption of alcohol (especially beer), seafood, red meat, and organ meats.
Chronic Stage:
In this stage, uric acid accumulates increasingly. Urate crystals deposit into Tophi (nodules/lumps) in the joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and severe pain. If not treated promptly, Gout can destroy joints, leading to permanent disability. This stage is accompanied by complications such as kidney failure and kidney stones due to the kidneys overworking to excrete excess uric acid from the blood.
3. Differentiating Gout from Other Conditions
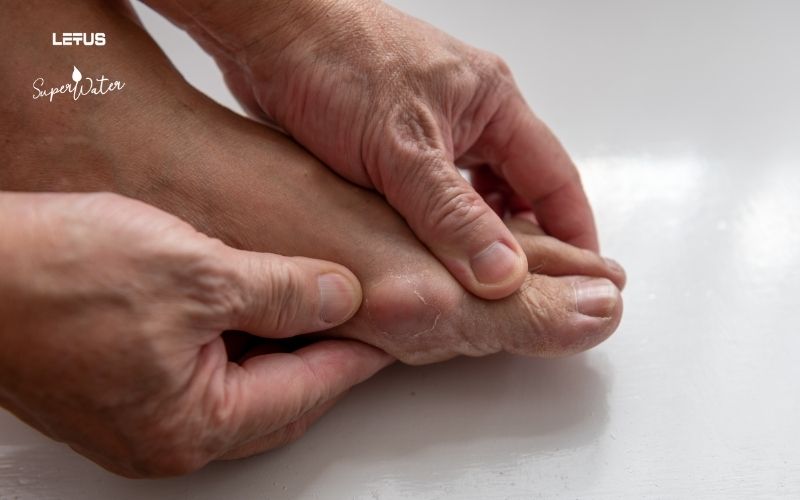
Most joint diseases originate from pain. Therefore, it is often easy to confuse the pain caused by Gout with the pain from other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or rheumatic fever.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily damages the joints. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, including joint cells. This leads to inflammation, swelling, pain, and joint stiffness.
Inflamed joints are typically symmetrical, and there is often persistent morning stiffness causing prolonged pain.
RA is not related to diet and is more common in middle-aged women, whereas Gout is more common in men and is strongly associated with daily food intake.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis usually occurs in areas like the fingers, knees, cervical spine, and hips. Clinically, OA pain differs from Gout pain: it occurs in multiple joints, the severity is milder, and it is long-lasting but without inflammation, swelling, or redness.
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body, including heart and joint tissues. This leads to joint pain, especially in large joints like the knees, hips, and shoulders, joint swelling, fever, fatigue, headaches, and rashes.
The fundamental difference between inflammation from rheumatic fever and Gout is that rheumatic fever typically occurs in adolescents, and its cause is usually an upper respiratory tract infection.
4. Gout Treatment Methods

1. Controlling Diet and Lifestyle for Gout Patients:
Diet can significantly affect blood uric acid levels. People with Gout should avoid purine-rich foods, a substance that can be metabolized into uric acid in the body.
- Avoid purine-rich substances such as: animal offal, meat, fish, shrimp, crab, etc. It is acceptable to eat eggs, fruits, and limit meat intake to no more than 150 grams per day.
- Do not drink alcohol; maintain a healthy weight, and engage in regular, moderate exercise.
- Drink plenty of water, about 2–4 liters per day, especially the highly permeable Letus SuperWater which neutralizes uric acid.
- Avoid medications that increase blood uric acid, and avoid factors that trigger acute Gout attacks, such as stress or trauma.
2. Medical Treatment (Pharmacological)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Used during the acute Gout attack phase to reduce inflammation.
- Uric acid-lowering drugs: Used during the chronic phase to prevent recurrent acute Gout attacks.
3. Surgical Treatment (Non-Pharmacological)
Surgical removal of Tophi is indicated in cases of:
- Gout complicated by ulcers or severe inflammation.
- Infected Tophi, ruptured, and inflamed Tophi.
- Large Tophi affecting mobility or for cosmetic reasons.
When undergoing surgery, colchicine is needed to prevent the onset of an acute Gout attack, combined with uric acid-lowering medication.
4. Gout Treatment with Alkaline Hydrogen Water

Hydrogen-rich alkaline water may support Gout treatment in the following ways:
- Neutralization and Excretion: Hydrogen-rich alkaline water helps enhance the neutralization and excretion process of uric acid in the blood and helps prevent the formation of Urate crystals.
- Increased Renal Uric Acid Excretion: Hydrogen, due to its microscopic molecule size, may help enhance kidney function, thereby assisting the kidneys in eliminating uric acid from the body more effectively.
- Antioxidant Effect: Hydrogen is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are one of the causes of inflammation and joint pain, which are key symptoms of Gout.
- Reduced Gout Pain: Alkaline water has been shown to have a positive effect on the body, which may be related to its ability to neutralize or even eliminate free radicals present in cells, thus preventing oxidative damage. Furthermore, consuming alkaline water helps balance acid-base levels, leading to better hydration, reducing pain and inflammation for Gout patients.
Here are some ways for Gout patients to supplement with hydrogen-rich alkaline water:
- Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Alkaline Water: This is the most common way to supplement with hydrogen. Hydrogen water can be purchased pre-packaged or extracted from a hydrogen water electrolyzer.
- Hydrogen-Rich Alkaline Water Baths: Bathing in hydrogen water may also help reduce joint pain and inflammation in Gout patients.
- Using Hydrogen-Rich Alkaline Water Supplements: Currently, there are several hydrogen supplements on the market, including pills, drinks, creams, etc.
- Drinking hydrogen-rich alkaline water is considered the most common and suitable method today. Daily consumption of hydrogen-rich water may help lower blood uric acid and effectively stabilize and improve Gout.
- Take medication as prescribed by a doctor.
- Maintain a proper diet and lifestyle.
- Engage in moderate exercise and rest appropriately.
- Drink Letus SuperWater.
- Visit the doctor regularly.



