1. What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that impacts motor function and progressively worsens over time.
The disease occurs due to the damage or death of nerve cells, known as neurons, in the basal ganglia of the brain. This brain region plays a crucial role in controlling movement. The primary cause of the symptoms is the decline in these nerve cells, leading to a shortage of Dopamine. Dopamine is a vital neurotransmitter that helps control body movements.
Therefore, suffering from Parkinson’s disease impairs a person’s ability to move, control muscles, and maintain balance.
Currently, the exact cause of the aging process in the nervous system that leads to Parkinson’s disease remains unknown. However, individuals with Parkinson’s disease often have a high level of free radicals (oxidative stress) in their bodies, which is believed to be a major factor contributing to the body’s aging, especially in nerve cells.
Oxidative stress, or free radicals, damages and weakens the neurons in the basal ganglia, causing them to produce very little Dopamine. This insufficient amount of Dopamine impairs signal transmission between nerve cells, leading to the manifestations of Parkinson’s disease, such as memory decline, motor dysfunction like hand tremors, stiffness in movement, and increased risk of falling.
2. Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease typically develop over a long period and can be subtle and difficult to recognize initially. People with PD usually progress through the following stages:
Stage 1: Symptoms usually occur on only one side of the body. Mild numbness and tremors appear, along with occasional muscle stiffness that may only be noticeable upon close observation.
Stage 2: Symptoms affect both sides of the body, and gait changes are evident. The person clearly feels tremors and difficulty moving in their arms, legs, and other organs on both sides. Facial expressions become more limited (mask-like face). The progression from Stage 1 to Stage 2 can take anywhere from a few months to several years.
Stage 3: Motor reflexes are reduced, and maintaining balance in daily activities becomes challenging. If detected and treated promptly, symptoms may improve.
Stage 4: Movement is significantly limited; the person can only walk short distances. Movements are extremely slow, standing for even a short time is difficult, and moving requires significant assistance and care from family and caregivers.
Stage 5: The person is unable to walk independently due to severe joint stiffness, is bedridden, or requires a wheelchair, becoming entirely dependent on others. At this point, the effectiveness of various treatment medications often diminishes.
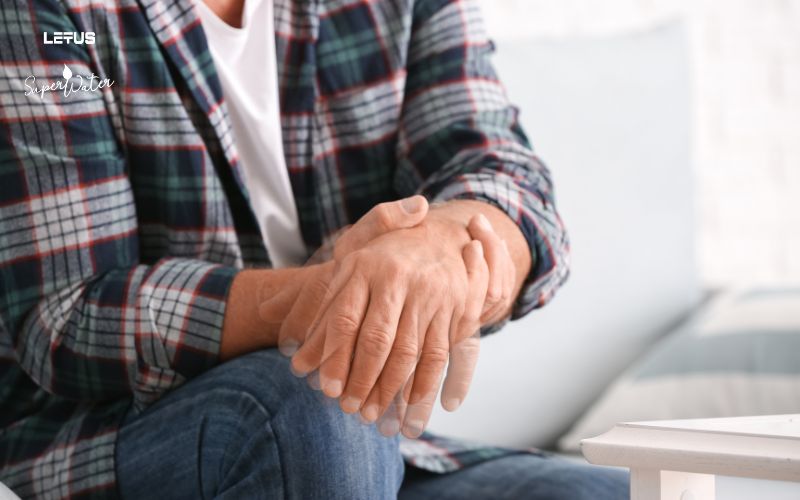

Common Symptoms and Manifestations of Parkinson’s Disease
The common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- Resting Tremor: Tremors occurring in one side of the body (typically an arm, leg, or finger) when the person is at rest.
- Rigidity (Increased Muscle Tone): Muscles become stiff and difficult to move.
- Bradykinesia (Slowness of Movement): Movements are slow and difficult, especially when initiating walking.
- Difficulty with Balance and Gait.
- Speech Changes: Voice becomes soft (hypophonia), monotone, and articulation is difficult.
- Emotional Changes: Emotions are easily altered, including irritability and depression.
3. Dangerous Complications of Parkinson’s Disease
Motor Complications
- Increased Risk of Falls: Due to loss of balance, muscle stiffness, and slowness, people with PD are highly prone to falls, which can cause severe injuries such as bone fractures and head trauma.
- Dysphagia (Difficulty Swallowing): Can lead to choking, malnutrition, and aspiration pneumonia (pneumonia caused by food/liquid entering the lungs).
- Sleep Disorders: Insomnia, poor sleep quality, snoring, and REM sleep behavior disorder, all of which affect overall health and quality of life.
- Pneumonia: Due to difficulty swallowing, aspiration, and reduced physical activity.
- Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores): Occur in patients who are bedridden for long periods.
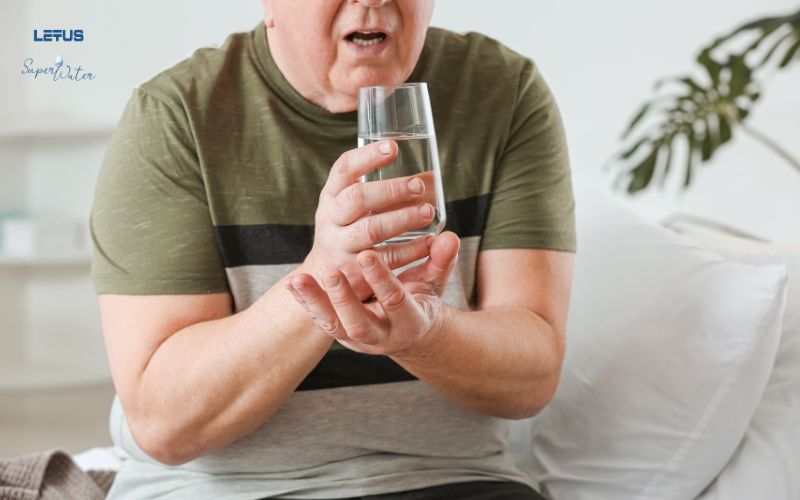

Psychiatric and Mental Complications
- Depression: Very common in people with PD, affecting quality of life and potentially leading to suicidal thoughts.
- Anxiety: Makes it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Hallucinations and Delusions: Often occur as the disease progresses, causing confusion, fear, and impacting social relationships.
- Behavioral Disorders: Such as agitation, aggression, and impulsivity.
Other Complications
Besides the psychological and motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, other complications include:
- Malnutrition: Due to difficulty swallowing and reduced appetite.
- Constipation: Caused by reduced mobility, improper diet, and certain medications.
- Urinary Incontinence: Due to pelvic floor muscle dysfunction.
- Cognitive Impairment: Occurs in the later stages of the disease.

Risk Factors that Increase Complications:
- Advanced Age: Older adults have a higher risk of complications.
- Extended Duration of the Disease: The more advanced the disease, the higher the risk of complications.
- Poor Overall Health: Co-existing conditions like cardiovascular disease or diabetes increase the risk of complications.
- Improper Medication Use: Can cause serious side effects.
To minimize complications, patients need to:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, and drink enough water.
- Exercise regularly: Helps improve movement and general health.
- Use medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor: Do not independently increase, decrease, or stop the medication.
- Have regular health check-ups: Helps in early detection and timely treatment of complications.
- Seek support from family and the community: Helps the person overcome difficulties and maintain a positive life.
4. Can Early Treatment Improve Parkinson’s Disease?
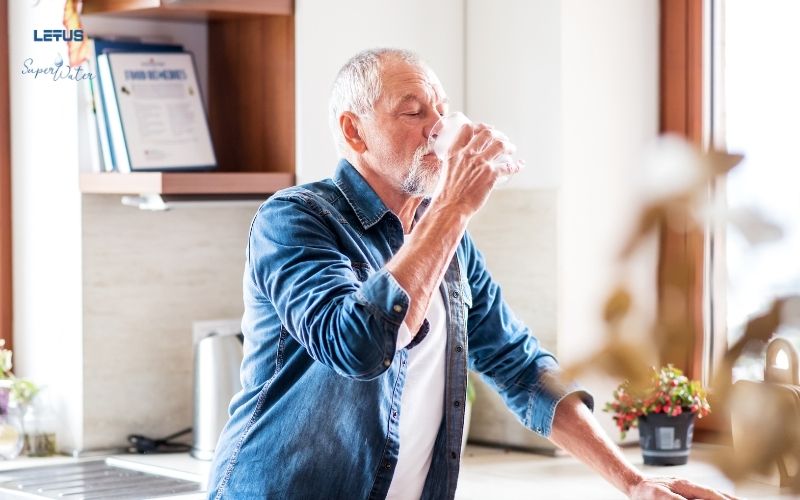

If detected and treated promptly, we can improve the condition of Parkinson’s disease, although there is currently no method that can completely cure it.
Common treatment methods for Parkinson’s disease include: medication, physical therapy and rehabilitation, surgery, and stem cell injections. However, these methods are long-term and require significant support from family members.
Recently, the application of Hydrogen in disease treatment has emerged as an effective solution. Hydrogen acts as a selective antioxidant for cells, inhibiting the process of oxidative stress and cellular damage, thereby protecting nerve cells from aging.
Researchers studying Parkinson’s disease have discovered that drinking hydrogen-rich water, even at concentrations as low as 5%, reduces symptoms of the disease by lessening oxidative stress. Research shows that molecular hydrogen has blocked both the development and progression of nigrostriatal degeneration (which causes Parkinson’s symptoms).
“Molecular Hydrogen prevented the loss of dopamine cells by protecting the nerves. Our study shows that hydrogen water has the potential to slow the development and progression of Parkinson’s disease.” – Research by Fu Y, Ito M, Fujita Y, et al., titled “Molecular hydrogen is protective against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nigrostriatal degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease“.
Monitoring the manifestations of Parkinson’s disease and supporting its improvement every day is essential to enhance the quality of life for the patient.
Letus SuperWater stabilizes HbA1c index within 90 days!



