Diabetes is a chronic, long-term disease. The causes of diabetes are often multifactorial, but the main manifestation is a persistent elevation in blood sugar (glucose) levels. Letus Water invites you to learn about the causes of diabetes and ways to manage this condition in the information below.
1. Understanding the Causes of Diabetes
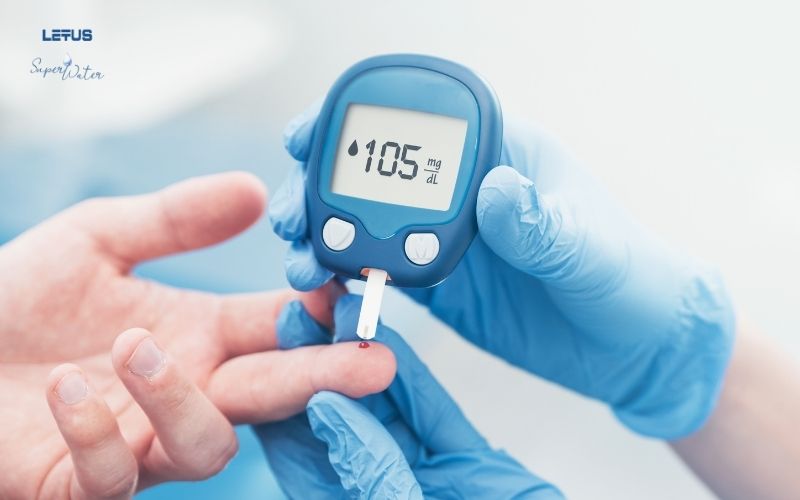
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic disease caused by a disturbance in insulin metabolism (the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin, or the insulin is weakened/ineffective, leading to cells not being able to absorb insulin), resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Depending on the causes of diabetes, the condition can be divided into three common types: Type 1 Diabetes (often called Insulin-Dependent Diabetes), Type 2 Diabetes (formerly known as Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes), and Gestational Diabetes (which some expectant mothers develop during pregnancy).
In addition, diabetes can also be caused by genetic defects, the use of certain medications or chemicals like Glucocorticoids, HIV/AIDS treatment, or following tissue transplantation.
Diabetes is an extremely dangerous condition. If you have it, you are twice as likely to develop cardiovascular disease as a healthy person. The risk of foot ulcers and subsequent amputation is 10 times higher, along with numerous other chronic complications affecting the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and skin. Understanding the causes of diabetes and the necessary information will equip you to manage the condition effectively.
2. The Underlying Causes of Different Types of Diabetes

Based on the different causes of diabetes, the condition is categorized as follows:
-
Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the pancreas typically produces very little or no insulin. The minimal or absent insulin prevents cells from having the catalyst needed to absorb glucose.
-
Type 2 Diabetes, in contrast, is primarily associated with oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals. People with Type 2 Diabetes have an excess production of free radicals in their bodies compared to antioxidants. These free radicals can cause various problems, such as cell damage, which makes cells less sensitive to insulin (insulin resistance) and impairs the function of the pancreas (leading to the production of ineffective insulin). Over time, both insulin and the cells become less sensitive and lose their ability to work together to metabolize glucose. Therefore, in patients with Type 2 Diabetes, blood glucose levels are high, and the existing insulin is not being utilized effectively.
-
Gestational Diabetes (usually occurs only during pregnancy): This is due to insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy, typically appearing in pregnant women from the 24th week onward, with no prior evidence of Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes.
Each type of diabetes has different characteristics. Understanding this information helps clarify the specific nature of the condition, leading to different treatment approaches.
3. Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes

For people with Type 1 Diabetes, common symptoms may include:
-
Frequent Hunger and Fatigue even after eating: This is the most noticeable sign because a lack of (or near absence of) insulin prevents cells from absorbing blood sugar and converting it into energy for the body.
-
Frequent Urination and Constant Thirst: A healthy person usually urinates about 4-7 times a day. The body normally reabsorbs sugar as it passes through the kidneys. When you have diabetes, blood sugar is so high that the kidneys must continuously flush it out through urination. That is why people with diabetes drink a lot of water and must urinate frequently.
-
Unexplained Weight Loss despite increased eating: Most food is converted into glucose, which cells absorb and turn into energy. People with diabetes cannot absorb glucose, so even if they eat a lot, they still lose weight.
-
Blurred Vision: The body losing more water to eliminate sugar, combined with high blood sugar levels, causes the retinal layer of the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision and reduced eyesight.

For people with Type 2 Diabetes, symptoms often develop silently, or there may be no noticeable symptoms at all. However, Type 2 Diabetes can still manifest with warning signs:
-
Yeast Infections: Red, moist, itchy patches of skin, sometimes with small blisters around them. Yeast feeds on glucose, so these infections often thrive in any moist skin fold, such as between fingers/toes, under the breasts, or in the genital area.
-
Slow-Healing Sores or Cuts, Increased Susceptibility to Infection: High blood glucose levels damage the nerves, often causing tingling or numbness in the hands and feet (neuropathy). When you have diabetes, the immune system is impaired, making wounds difficult to heal and increasing the risk of infection.
4. Diabetes Complications: Understanding the Danger
Diabetes causes significant damage to vital organs, especially the blood vessels, heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and mouth.
Acute, Highly Dangerous Complications:
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Occurs when a patient takes too much blood-sugar-lowering medication, skips meals, consumes alcohol, eats too little, or exercises intensely without consuming enough energy.
When blood sugar drops too low (below approximately 3.6 mmol/L or 65 mg/dL), symptoms include intense hunger, sluggishness, fatigue, shaking hands and feet, sweating, dizziness, and a rapid heartbeat. If not recognized and treated immediately, hypoglycemia can lead to a coma.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar) and Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): When cells cannot absorb glucose, the body uses hormones to break down fat for energy. This process creates a large amount of harmful substances called acids and ketones. Over time, this leads to frequent thirst and urination (the body flushing out toxins and sugar), fatigue, and breath with a fruity, fermented odor (due to ketones in the blood). More severely, it can lead to loss of consciousness or even death (DKA). Sudden, very high blood sugar can also cause a coma and requires immediate emergency care.
Chronic, Highly Dangerous Complications:
-
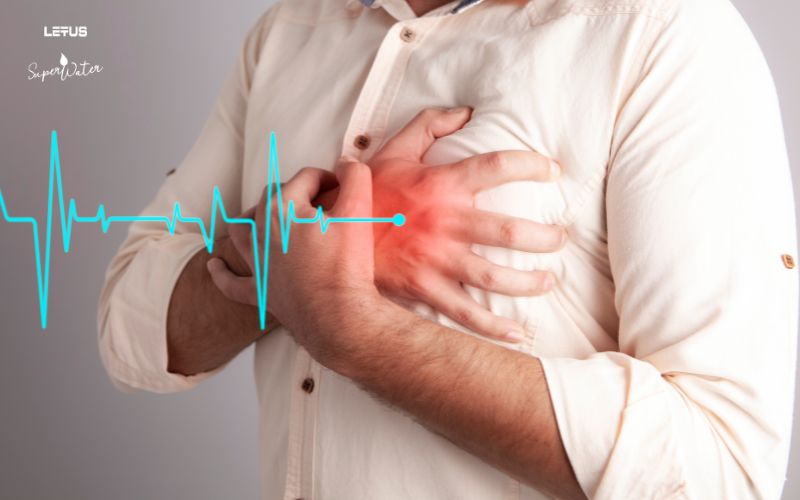
Heart and Vascular Disease: High blood sugar damages the cardiovascular system, causing angina (chest pain), and increasing the risk of stroke or heart attack.
-
Vision Loss (Diabetic Retinopathy): Caused by damaged small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to sudden vision loss, glaucoma, cataracts, and retinopathy.
-
Kidney Issues (Diabetic Nephropathy): High blood sugar forces the kidneys to overwork, leading to chronic kidney failure over time. Symptoms include swelling in the hands and feet.
-
Nerve Damage (Diabetic Neuropathy): Causes pain, burning sensations, or loss of sensation in the feet, hands, and internal organs, potentially leading to gastroparesis, sexual dysfunction, dizziness, and fainting.
-
Oral Health Problems: People with diabetes are prone to dry mouth, gum inflammation, painful chewing, and even tooth loss due to a weakened immune system and slow wound healing.
-
Macrovascular Complications: Related to coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and stroke.
-
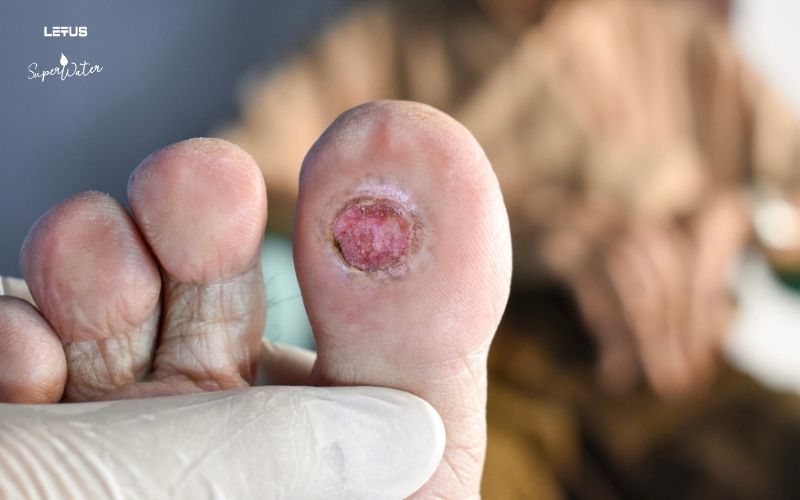
Infections: Skin, urinary tract, tuberculosis, and Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Peripheral vascular disease, especially in the lower limbs, often leads to gangrene and amputation, a complication that severely affects the patient’s health.
-
Microvascular Complications: Glomerular disease (kidney), neuropathy (nerve), and retinopathy (eye).

5. Managing Diabetes and Essential Information
Diabetes is characterized by persistently high blood sugar, causing fatigue, weakness, slow wound healing, and dangerous complications.
The following steps can help stabilize blood sugar levels:
-
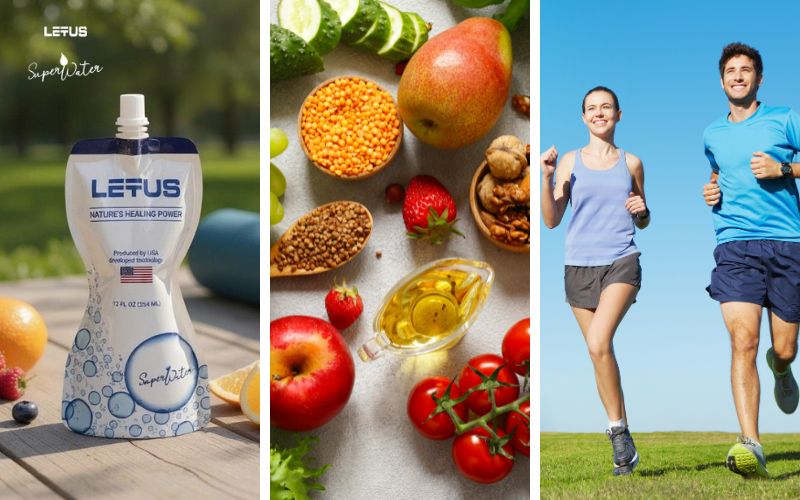
Healthy Eating: Focus on a diet rich in fiber, low in sugar, and low in saturated fat. Limit refined sugar, sweets, and high-starch foods. Increase your intake of vegetables, whole fruits, whole grains, and lean protein.

-
Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily to improve your body’s sensitivity to insulin and help control blood sugar.
-
Lose Weight If Needed: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly improve blood sugar control. Even small changes in weight can yield great benefits.
-
Maintain a Balanced Lifestyle: Stress, anxiety, and sleep deprivation can elevate blood sugar. Try to keep a relaxed, confident attitude, and share your feelings with family to maintain a comfortable state of mind daily.
-
Regular Check-ups: To monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
-
Maintain Prescribed Medications: To control blood sugar and prevent potential complications.
-
Limit Alcohol and Tobacco: Both can negatively affect your overall health and increase the risk of diabetes complications. Limit or avoid them entirely.

6. Regular Medical Visits and Essential Information
Adhere to your doctor’s instructions for medication use; do not stop using medication or change the dosage on your own. Also, ensure you are fully vaccinated (flu, measles, mumps, rubella, pertussis, pneumonia, etc.) to protect yourself against diabetes-related complications and other illnesses.
Your doctor can adjust your therapy based on the disease progression and your health status. Adhering strictly to medication use and other treatments can reduce the risk of complications and improve your quality of life.
Regular check-ups allow the doctor to monitor the disease’s progress and detect any early signs of potential complications. This helps adjust the treatment plan and prevent the development of serious health issues.
Thus, controlling blood sugar and following your doctor’s advice not only manages diabetes but also reduces the risk and prevents dangerous complications.

Healthy Habits for Diabetes Improvement:
-
Stop Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of cardiovascular complications, stroke, and other diabetes-related issues.
-
Educate Yourself: Learn about diabetes and self-care. Attend diabetes education classes if possible.
-
Reduce Stress: Practice yoga, meditation, listen to music, and talk with family and friends, as stress can raise blood sugar.
-
Drink Letus Water daily (it can be used as a substitute for regular drinking water) to help maintain stable blood sugar levels (as suggested by Letus Water).
The danger of diabetes lies in the difficulty of controlling blood sugar levels. Therefore, knowing the causes of diabetes can help you reduce the glucose intake into your body. After understanding the causes of diabetes, we can apply a scientific regimen for care, diet, hydration, and lifestyle to keep blood sugar stable, which will help people with diabetes live a healthier and more confident life every day.



