1. Who is at Risk for Gout?
The prevalence of Gout is approximately 1 in 200 adults. The disease can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. However, it is more common in men aged 30–50 and women in the post-menopausal stage. Gout rarely occurs in young people and children.
Certain groups have a higher incidence of Gout:
- Men over 40: Statistics show that over 80% of Gout patients are men over 40, often due to a diet high in protein: animal offal (organ meats), and excessive consumption of red meat (such as beef). Additionally, an unhealthy lifestyle, including a lack of exercise, frequent alcohol consumption (especially beer), and smoking, contributes to the risk.
- Women Postpartum: Postpartum women undergo body changes, and due to a diet supplemented with a lot of nutrients, the body’s fat content can be higher than normal.
- Women Approaching Menopause: Experience a decline in the hormone Estrogen, which causes a disturbance in uric acid metabolism.
- Overweight or Obese Individuals: Have difficulty excreting uric acid.
- Family History of Gout: Currently, there are 5 genes associated with Gout, and most are likely to be inherited. Therefore, the chance of developing Gout may be due to a family member having had the disease.
- People with an Unscientific Diet: Low intake of green vegetables and high consumption of seafood, red meat, and animal offal.
2. How Does Gout Affect Quality of Life?
Long-term Gout can lead to complications such as Tophi and joint deformity, causing excruciating pain that significantly affects daily life:
- Limited Mobility: Pain and swelling make it impossible for Gout sufferers to move quickly or perform high-calorie-burning exercises.
- Sleep Quality: Gout attacks often occur at night, accompanied by discomfort and pain that directly impact sleep or change in resting position.
- Mental Impact: Recurrent Gout pain leads to constant anxiety and prolonged stress.
- Mandatory Dietary Restrictions: Gout patients are forced to severely restrict many foods and change life habits.
- Impact on Work Performance: Gout sufferers may find it challenging to maintain focus and efficiency at work due to the pain and swelling.
- Long-Term Effects: If left uncontrolled, Gout can destroy and deform joints, leading to disability.
Therefore, methods for relieving Gout pain are continually researched and applied to prevent disease progression and provide comfort to the patient.
3. Secrets to Preventing and Relieving Gout Pain
3.1 Immediate Relief for a Gout Attack
When Gout symptoms appear, quick pain relief is the top priority. Here are some measures you can apply:
- Cold Compress: Wrap ice in a soft towel and apply it to the swollen, painful joint for about 20–30 minutes to reduce swelling and pain.
- Elevate the Joint: Raise the swollen joint or lie down completely to reduce pressure on the joint.
- Rest: Avoid strenuous activity when the joint is inflamed.
- Use Pain Medication: Take pain and anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed by a doctor. (This may include Colchicine: a specific medication for Gout that is very effective in reducing joint inflammation and pain. However, it must be used strictly according to the doctor’s dosage and instructions).
- Drink Plenty of Water, Especially Electrolyzed Alkaline Hydrogen Water: Alkaline hydrogen water produced through electrolysis has rapid permeability and can neutralize Uric Acid, reducing the formation of Urate crystals. Meanwhile, hydrogen can help improve swelling and inflammation, effectively relieving Gout pain.

3.2 Long-Term Gout Pain Reduction
To relieve Gout pain long-term and prevent recurrence, you need to combine the following measures:
Proper Nutrition to Stabilize Uric Acid Levels
- Limit Purine-Rich Foods: Red meat, animal offal, seafood, alcohol (especially beer), and carbonated drinks.
- Increase Green Vegetables and Fruits: Provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Use Less Refined Sugar: Replace with natural sugars found in vegetables and grains.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Drink 2.5–3 liters of water daily, especially Letus SuperWater, to increase uric acid excretion within 45 minutes. This can improve soreness and reduce numbness in the hands.
- Minimize Alcoholic Beverages: Especially beer and hard liquor.
- Limit Beverages: Coffee, tea, and sugary carbonated drinks.
Some Foods Good for Gout Patients:
- Cherries: Help reduce inflammation and lower uric acid concentration.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Kale, cabbage, broccoli, etc.
- Fruits: Oranges, lemons, grapefruit, pineapple, etc.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, etc.
- Low-Fat Milk: Provides calcium and protein.
Foods to Avoid:
- Red Meat: Beef, pork, etc.
- Animal Offal: Liver, heart, kidney, etc.
- Seafood: Shrimp, crab, clams, oysters, etc.
- Alcohol: All alcoholic beverages.
- Carbonated Drinks: Soft drinks, energy drinks, etc.
Weight Management
- A healthy weight helps reduce elevated uric acid and prevents placing undue pressure on the joints.
Appropriate Exercise
- Regular exercise helps strengthen cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation. However, avoid overexertion.
Uric Acid-Lowering Medication
- Helps reduce uric acid concentration in the blood, preventing recurrent Gout attacks.
Treatment of Co-existing Conditions
- If you have conditions like diabetes or hypertension, treating them effectively will help control Gout better.
Consistent Medication Adherence as Prescribed by a Doctor
- Following your doctor’s instructions can improve your condition and allow the medical team to accurately monitor your health, leading to effective treatment plans.
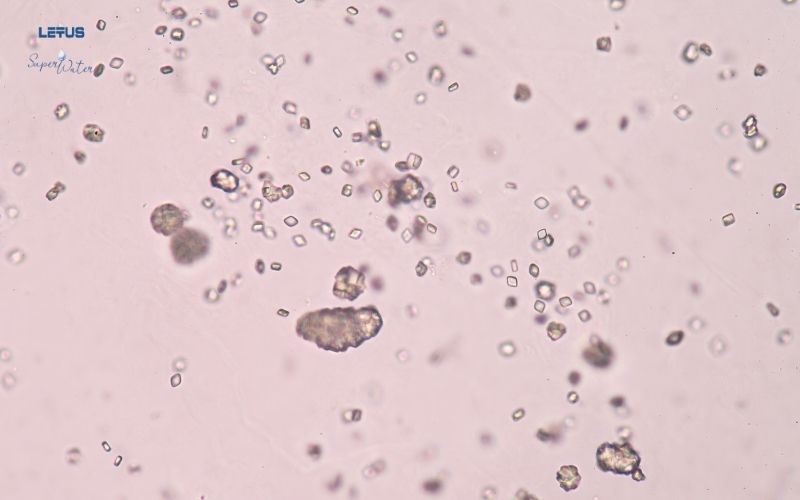
Drink Plenty of Water, Especially Alkaline Water
Drinking plenty of electrolyzed alkaline hydrogen water can neutralize uric acid, reduce the deposition of Urate crystals in the joints, and effectively relieve Gout pain.
Healthy Lifestyle
Engage in daily, moderate physical exercise.
Exercise and participate in outdoor activities to boost health, avoiding high-intensity work.
Follow the doctor’s instructions; do not self-medicate or stop prescribed medication without consulting your doctor.
Schedule regular follow-up appointments for thorough monitoring of your condition.
Effectively treat conditions that cause secondary Gout, such as kidney failure and other metabolic diseases.
3.3 Important Notes for Gout
- Seek a Doctor’s Advice: For an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
- Consistent Treatment: Gout is a chronic disease requiring long-term treatment for control.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequently check your health to monitor the disease status and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
During an acute Gout flare-up, if you cannot relieve the Gout pain, you need to contact a doctor and go to the nearest medical facility for timely treatment.
4. The Best Time to Check Uric Acid

The best times for a blood uric acid test for a Gout patient are:
- During the acute phase of the disease: When Gout symptoms like swelling, pain, and redness in the joint are present. At this time, the uric acid concentration in the blood is usually at its peak. The test result will help the doctor accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe a suitable treatment method.
- During the post-acute phase of the disease: When the symptoms have lessened or disappeared. At this time, the blood uric acid concentration may be lower than during the acute phase but still needs to be monitored to ensure no recurrence.
- When undergoing Gout treatment: A blood uric acid test helps the doctor evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment method and adjust the medication if necessary.
In addition, Gout patients should have their blood uric acid checked periodically, approximately every 6 months. This helps the doctor detect any changes in uric acid concentration early and intervene promptly.
To ensure accurate blood uric acid test results, patients should note:
- Do not eat or drink for 8–10 hours before the test.
- Do not consume alcohol, smoke, or use stimulants within 24 hours before the test.
- If you are taking medication, you must inform your doctor for advice on whether to stop the medication before the test.

Letus SuperWater is alkaline hydrogen water that can help reduce Urate formation causing Gout pain and reduce inflammation and swelling to soothe acute Gout attacks: Reduces daily uric acid levels, Provides rapid relief from Gout pain.



